Optimization of Logistics and Industrial Wastewater Treatment System Using Grey Wolf Optimization Algorithm
Keywords:
Industrial wastewater collection, closed-loop supply chain, sustainability requirements, Grey Wolf Optimization algorithmAbstract
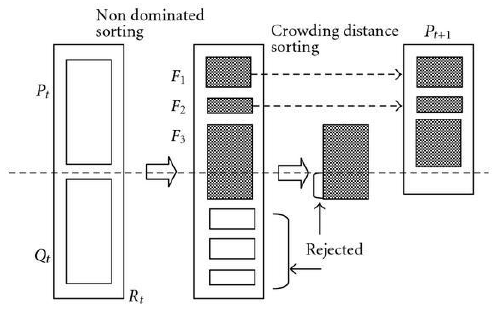
Industrial wastewater collection involves the systematic gathering, transportation, and disposal of waste generated by industrial activities. This process is crucial for maintaining environmental health and safety, as industrial wastewater may contain hazardous materials that require special management. Effective waste collection strategies not only help reduce pollution but also contribute to the recycling and reuse of materials, thereby conserving resources. Advanced technologies and adherence to regulations play key roles in ensuring the efficient and sustainable management of industrial wastewater. Considering the role of closed-loop supply chains in industrial wastewater collection, this paper presents a bi-objective mathematical model aimed at minimizing both the costs associated with surface wastewater collection and the environmental pollution from waste discharge. The model is solved using the multi-objective Grey Wolf Optimization algorithm. The results show that the model extends the network by including more vehicles and increasing the distances between locations. This optimal collection model ensures that wastewater is gathered from candidate sites by the vehicles within the network. Additionally, sensitivity analysis reveals that the most influential parameters on the model's objectives are the transportation cost per unit distance, the penalty for vehicle usage, and the revenue per kilogram of treated wastewater.
References
Y. Zhao et al., "Bullwhip effect mitigation of green supply chain optimization in electronics industry," Journal of Cleaner Production, vol. 180, pp. 888-912, 2018, doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.01.134.
M. A. Dzikriansyah, I. Masudin, F. Zulfikarijah, M. Jihadi, and R. D. Jatmiko, "The role of green supply chain management practices on environmental performance: A case of Indonesian small and medium enterprises," Cleaner Logistics and Supply Chain, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 100100-100100, 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.clscn.2023.100100.
A. Rashid, N. Baloch, R. Rasheed, and A. H. Ngah, "Big data analytics-artificial intelligence and sustainable performance through green supply chain practices in manufacturing firms of a developing country," Journal of Science and Technology Policy Management, 2024.
A. S. Abir, I. A. Bhuiyan, M. Arani, and M. M. Billal, "Multi-Objective Optimization for Sustainable Closed-Loop Supply Chain Network Under Demand Uncertainty: A Genetic Algorithm," arXiv preprint arXiv:2009.06047, 2020, doi: 10.1109/ICDABI51230.2020.9325648.
M. Arani, X. Liu, and S. Abdolmaleki, "Scenario-based simulation approach for an integrated inventory blood supply chain system," in 2020 Winter Simulation Conference (WSC), 2020: IEEE, pp. 1348-1359, doi: 10.1109/WSC48552.2020.9384018.
S. Mohtsham and S. K. Tharollahi, "The relationship between green supply chain components and productivity in organizations," (in Persian), Management and Entrepreneurship Studies, vol. 2, no. 4, pp. 115-106, 2015.
S. Abbasi, M. Daneshmand-Mehr, and A. Ghane Kanafi, "Green closed-loop supply chain network design during the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic: a case study in the Iranian automotive industry," Environmental Modeling & Assessment, vol. 28, no. 1, pp. 69-103, 2023, doi: 10.1007/s10666-022-09863-0.
M. Zengin, S. H. Amin, and G. Zhang, "Closing the Gap: A Comprehensive Review of the Literature on Closed-Loop Supply Chains," Logistics, vol. 8, no. 2, pp. 54-54, 2024, doi: 10.3390/logistics8020054.
S. Bhattacharya, K. Govindan, S. G. Dastidar, and P. Sharma, "Applications of artificial intelligence in closed-loop supply chains: Systematic literature review and future research agenda," Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, vol. 184, pp. 103455-103455, 2024, doi: 10.1016/j.tre.2024.103455.
S. H. Amin, G. Zhang, and M. N. Eldali, "A review of closed-loop supply chain models," Journal of Data, Information and Management, vol. 2, pp. 279-307, 2020, doi: 10.1007/s42488-020-00034-y.
M. Masanta, B. C. Giri, and P. Das, "Green consideration in a closed-loop supply chain model with imperfect inspection under learning impact," Journal of Cleaner Production, vol. 428, pp. 139201-139201, 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.139201.
M. Farrokh, A. Azar, G. Janaghi, and E. Ahmadi, "A novel robust fuzzy stochastic programming for closed loop supply chain network design under hybrid uncertainty," (in Persian), Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 2017, doi: 10.1016/j.fss.2017.03.019.
Y. T. Jung, N. C. Narayanan, and Y. L. Cheng, "Cost comparison of centralized and decentralized wastewater management systems using optimization model," Journal of Environmental Management, vol. 213, pp. 90-97, 2018, doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.01.081.
M. R. Kabir, M. S. Kamal, and M. Z. Islam, "An Improved Network Design of Open Loop Reverse Supply Chain," in 2021 International Conference on Automation, Control and Mechatronics for Industry 4.0 (ACMI), 2021: IEEE, pp. 1-6, doi: 10.1109/ACMI53878.2021.9528280.