Predicting EOR Efficiency Under Harsh Reservoir Conditions Using Machine Learning Methods
Keywords:
Enhanced oil recovery, machine learning, harsh reservoir conditions, gradient boosting, reservoir characterization, chemical EOR prediction, SHAP interpretabilityAbstract
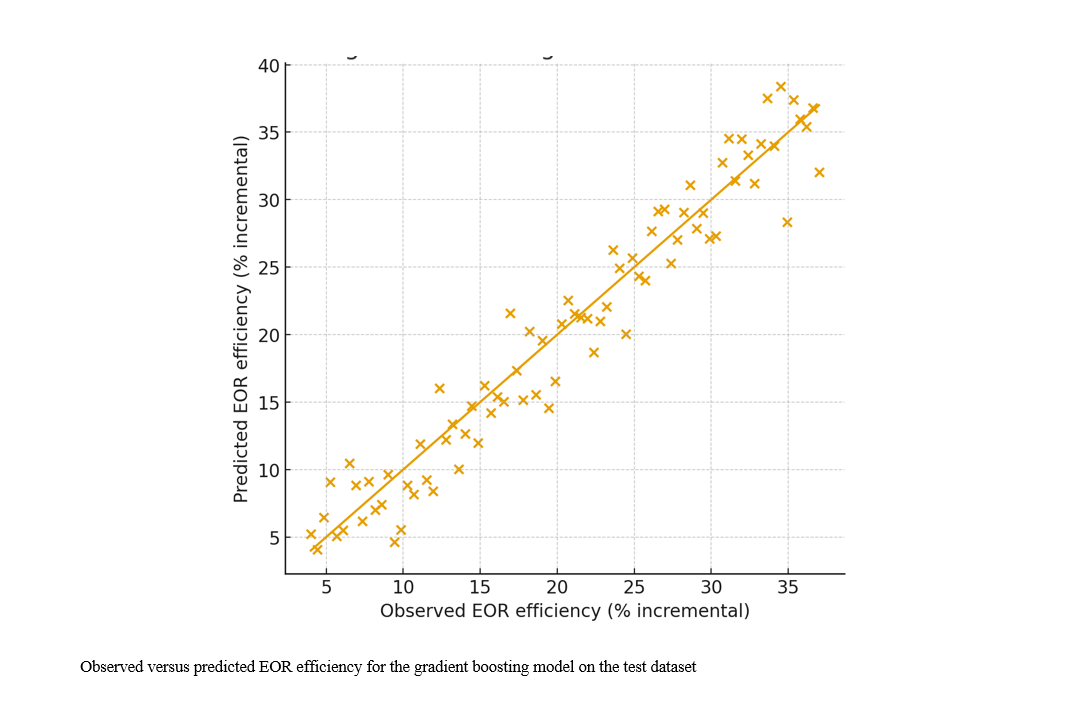
This study aimed to develop and validate a machine learning model capable of accurately predicting enhanced oil recovery (EOR) efficiency under harsh reservoir conditions. The study employed a quantitative, data-driven design using reservoir, petrophysical, and operational data collected from a wide range of high-temperature, high-salinity, and heterogeneous reservoirs. Data sources included core-flooding experiments, reservoir simulations, and field-reported EOR project results. All variables were preprocessed through scaling, outlier treatment, and missing-value handling. Machine learning models—including Random Forest, Gradient Boosting, Support Vector Regression, and Artificial Neural Networks—were trained using an 80/20 train–test split with repeated cross-validation. Feature importance was assessed using SHAP values to ensure interpretability. Model performance was evaluated using RMSE, MAE, and R² metrics to determine predictive accuracy under extreme reservoir conditions. Gradient Boosting achieved the highest predictive accuracy (R² = 0.91; RMSE = 3.05), outperforming Support Vector Regression and demonstrating slightly better generalization than Random Forest and Artificial Neural Networks. Across all models, reservoir temperature and formation water salinity emerged as the strongest negative predictors of EOR efficiency, while optimized polymer and surfactant concentrations consistently showed positive predictive effects. Permeability and porosity had moderate but meaningful influences, while brine hardness and injection rate contributed smaller, variable effects. SHAP interpretability confirmed that the model’s predictive directions aligned with known physicochemical behaviors in harsh reservoir environments. Machine learning methods—particularly ensemble models—provide reliable, interpretable, and highly accurate tools for predicting EOR efficiency in harsh reservoir environments, offering significant potential to support screening, optimization, and decision-making for chemical and gas-based EOR projects.
References
K. Al-Azani, A. F. Ibrahim, S. Elkatatny, and D. A. Shehri, "Prediction of Foam Half-Life Time Using Machine Learning Algorithms for Enhanced Oil Recovery and CO2 Sequestration," Energy & Fuels, vol. 39, no. 19, pp. 8989-9007, 2025, doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.5c01054.
P. Vaziri, S. Ahmadi, F. Daneshfar, B. Sedaee, H. Alimohammadi, and M. R. Rasaei, "Machine Learning Techniques in Enhanced Oil Recovery Screening Using Semisupervised Label Propagation," Spe Journal, vol. 29, no. 09, pp. 4557-4578, 2024, doi: 10.2118/221475-pa.
M. Derakhshan, "Oil Contracts from the Perspective of Sustainable Production and Enhanced Recovery: The Resistance Economy Approach," Islamic Economic Studies Scientific-Research Biannual, vol. 6, no. 2, 2014.
B. Mepaiyeda, M. Ezeh, O. A. Olafadehan, A. Oladipupo, O. S. Adebayo, and E. Osaro, "Integration of Machine Learning and Feature Analysis for the Optimization of Enhanced Oil Recovery and Carbon Sequestration in Reservoirs," 2025, doi: 10.26434/chemrxiv-2025-5v32t.
A. Abdulwarith, M. Ammar, and B. Dindoruk, "Prediction/Assessment of CO2 EOR and Storage Efficiency in Residual Oil Zones Using Machine Learning Techniques," Energies, vol. 18, no. 20, p. 5498, 2025, doi: 10.3390/en18205498.
B. Ahmed, A. Kasha, S. Patil, M. S. Aljawad, and M. S. Kamal, "Extensive Study on the Influencing Parameters of Sc CO2 Foam Viscosity for Enhanced Oil Recovery and Carbon Sequestration: A Machine Learning Approach," 2024, doi: 10.2118/219163-ms.
A. Akbari, "Machine Learning and Nanoparticles for Enhancing Condensate Recovery in Gas Condensate Reservoirs," The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2025, doi: 10.1002/cjce.70119.
A. Aliyev, S. Kalam, M. Riazi, and P. Pourafshary, "Prediction of Storage and Loss Modules of Preformed Particle Gels Using Machine Learning," 2025, doi: 10.2118/226944-ms.
S. B. Anieto, "Machine Learning Assisted Optimization of Carbon Capture and Storage in Oil and Gas Reservoirs Through Advanced Geomodelling," Harvard International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology, 2025, doi: 10.70382/hijert.v9i5.014.
M. N. Assaf, Q. Abdelal, N. M. Hussein, G. Halaweh, and A. Al‐Zubaidi, "Water Quality Monitoring and Management: Integration of Machine Learning Algorithms and Sentinel-2 Images for the Estimation of Chlorophyll-A," Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, vol. 11, no. 5, 2025, doi: 10.1007/s40808-025-02543-4.
C. Carpenter, "AI Approach Advances Predictive Precision in CO2 Minimum Miscibility Pressure," Journal of Petroleum Technology, vol. 77, no. 01, pp. 59-62, 2025, doi: 10.2118/0125-0059-jpt.
C. Carpenter, "Physics-Informed ML Improves Forecasting, Connectivity Identification for CO2 EOR," Journal of Petroleum Technology, vol. 77, no. 01, pp. 55-58, 2025, doi: 10.2118/0125-0055-jpt.
A. A. Elhadidy et al., "Smart Matrix Acidizing: Real-Time Skin Factor Prediction With AI," 2025, doi: 10.2118/225024-ms.
N. Fayyaz, "3D Structural Geomechanics and Machine Learning Based Petrophysical Evaluation of Proven and Mature Oilfield in Upper Indus Basin, Pakistan," 2024, doi: 10.56952/igs-2024-0665.
H. Fu, J. Xiu, L. Huang, L. Yi, Y. Ma, and S. Wang, "Evaluation of Oil Displacement by Polysaccharide Fermentation Broth of Athelia Rolfsii Under Extreme Reservoir Conditions," Molecules, vol. 30, no. 13, p. 2861, 2025, doi: 10.3390/molecules30132861.
H. Jing, H. Pan, J. Liu, and Z. Fang, "Deep-Learning Accelerated Phase Equilibrium Calculations for Compositional Simulation in Shale Reservoir," 2025, doi: 10.2118/223868-ms.
S. Kalam, M. R. Khan, M. Shakeel, M. Mahmoud, and S. A. Abu-Khamsin, "Smart Algorithms for Determination of Interfacial Tension (IFT) Between Injected Gas and Crude Oil – Applicable to EOR Projects," 2023, doi: 10.2118/213375-ms.
Z. Khursheed et al., "Comparative Study of Machine Learning and Artificial Neural Networks for Porosity and Permeability Prediction in Reservoir Characterization," 2025, doi: 10.2118/224836-ms.
S. Krishna, S. A. Irfan, S. Keshavarz, G. Thonhauser, and S. U. Ilyas, "Smart Predictions of Petrophysical Formation Pore Pressure via Robust Data-Driven Intelligent Models," Multiscale and Multidisciplinary Modeling Experiments and Design, vol. 7, no. 6, pp. 5611-5630, 2024, doi: 10.1007/s41939-024-00542-z.
N. Li et al., "Intelligent Method for PDC Bit Selection Based on Graph Neural Network," Applied Sciences, vol. 15, no. 18, p. 9985, 2025, doi: 10.3390/app15189985.
C. Liu, J. Wang, J. Wang, and A. Yarahmadi, "Accurate Modeling of Crude Oil and Brine Interfacial Tension via Robust Machine Learning Approaches," Scientific Reports, vol. 14, no. 1, 2024, doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-80217-4.
M. Maleki, A. Akbari, Y. Kazemzadeh, and A. M. Ranjbar, "Machine Learning Models for the Prediction of Hydrogen Solubility in Aqueous Systems," Scientific Reports, vol. 15, no. 1, 2025, doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-16289-7.
D. A. Mamykin, "Selection of Flow Diversion Technology for a Carbonate Reservoir Object," Petroleum Engineering, vol. 23, no. 5, pp. 31-42, 2025, doi: 10.17122/ngdelo-2025-5-31-42.
A. Moncada, E. W. Al-Shalabi, W. AlAmeri, M. Tembely, and E. S. Mathew, "A Comprehensive Machine Learning Approach for EOR Screening in Sandstone and Carbonate Reservoirs," 2024, doi: 10.2118/222011-ms.
M. Nagappan, S. Jayamurugan, and A. Kudiarasumani, "Advanced Prediction of Crop Water Requirements Using Machine Learning Models," International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Techno, pp. 2518-2523, 2025, doi: 10.38124/ijisrt/25feb1206.
S. O. Rab et al., "Machine Learning-Based Estimation of Crude Oil-Nitrogen Interfacial Tension," Scientific Reports, vol. 15, no. 1, 2025, doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-85106-y.
A. Talapatra, B. Nojabaei, and P. Khodaparast, "A Data-Based Continuous and Predictive Viscosity Model for the Oil-Surfactant-Brine Microemulsion Phase," 2024, doi: 10.2118/218134-ms.
S. A. Thabet, S. Lnu, A. Guezei, O. Ejehu, and R. G. Moghanloo, "Downhole Camera Runs Validate the Capability of Machine Learning Models to Accurately Predict Perforation Entry Hole Diameter," Energies, vol. 17, no. 22, p. 5558, 2024, doi: 10.3390/en17225558.
S. A. Thabet, A. A. El-Hadydy, and M. A. Gabry, "Machine Learning Models to Predict Pressure at a Coiled Tubing Nozzle's Outlet During Nitrogen Lifting," 2024, doi: 10.2118/218294-ms.
S. Thabet et al., "Prediction of Total Skin Factor in Perforated Wells Using Models Powered by Deep Learning and Machine Learning," 2024, doi: 10.2118/219187-ms.
S. Thabet et al., "Machine Learning Models to Predict Total Skin Factor in Perforated Wells," 2024, doi: 10.2118/218838-ms.
W. Wei, P. Lü, C. Zhu, P. Luo, and R. Mesdour, "Advanced Machine Learning Models for CO2 and H2S Solubility in Water and NaCl Brine: Implications for Geoenergy Extraction and Carbon Storage," Energy & Fuels, vol. 38, no. 12, pp. 11119-11136, 2024, doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.4c01423.
B. Yan and Y. Zhang, "Efficacy Gain From a Deep Neural Network-Based History-Matching Workflow," 2024, doi: 10.2118/220876-ms.
F. Su, J. Zhao, X. Wen, Y. Zhang, J. Han, and Y. Chen, "Machine Learning–Based Prediction of the Mechanical Response of Hydrate-Bearing Sediments Under Multifield Coupling," Spe Journal, pp. 1-18, 2025, doi: 10.2118/230308-pa.
A. D. Ogbu, K. A. Iwe, W. Ozowe, and A. H. Ikevuje, "Advances in Machine Learning-Driven Pore Pressure Prediction in Complex Geological Settings," Computer Science & It Research Journal, vol. 5, no. 7, pp. 1648-1665, 2024, doi: 10.51594/csitrj.v5i7.1350.
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Parsa Kazemihokmabad (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.











