Designing a Model for the Impact of Viral Marketing in Social Networks Using Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference Systems
Keywords:
Viral marketing, Social networks, ANFIS, Word-of-mouth marketing, ViralAbstract
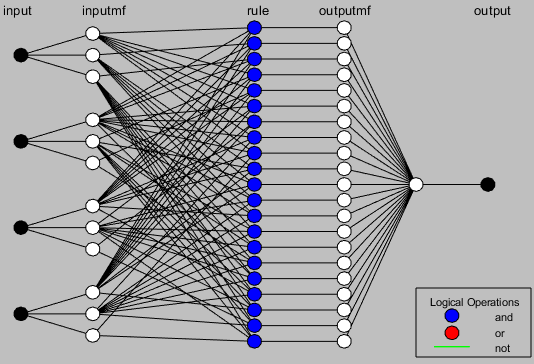
The aim of this study is to design a model for the impact of viral marketing in social networks using the Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS). This research utilizes the Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System due to its ability to implement human knowledge through concepts like timestamps and fuzzy rules, its nonlinear nature, adaptability, and superior accuracy compared to other methods in conditions with limited data. These features are among the most significant advantages of ANFIS systems. The MATLAB software was employed in the ANFIS framework to modify inputs and outputs. This research followed the steps of input fuzzification, fuzzy rule base development, fuzzy inference engine construction, aggregation phase, and defuzzification when employing the Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System. Value-based marketing relies on the principle that individuals who have used a product or service and had a positive experience share this experience with others, encouraging them to use the product or service as well. Viral marketing is, in a way, a form of partnership where an individual shares their experience with another person who needs the product or service. Due to its broad reach, low cost, high speed, and simplicity, companies can implement controlled viral marketing campaigns through principled and regulatory-compliant marketing efforts, thereby contributing to the growth of the company. This is because, within a short period, many people become familiar with the company and its brand name.
References
K. Motoki, S. Suzuki, R. Kawashima, and M. Sugiura, "A Combination of Self-Reported Data and Social-Related Neural Measures Forecasts Viral Marketing Success on Social Media," Journal of Interactive Marketing, vol. 52, pp. 99-117, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.intmar.2020.06.003.
J. Robles, M. Chica, and O. Cordon, "Evolutionary multiobjective optimization to target social network influentials in viral marketing," Expert Systems with Applications, vol. 147, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113183.
M. H. Al-Khasawneh, S. Al-Haddad, R. Mbaideen, R. Ghazi, T. Irshaid, and H. Alnaimi, "Investigating the impact of social media marketing on research online and purchase offline for fashion luxury brands," International Journal of Business Excellence, vol. 32, no. 1, pp. 25-49, 2024, doi: 10.1504/ijbex.2024.135933.
L. Jiang, "The Extent Social Media Marketing Is Contributable to Customer Based Brand Equity of Luxury Brands," pp. 485-497, 2024, doi: 10.2991/978-94-6463-408-2_55.
S. Mukherjee, M. K. Das, and T. K. Chakraborty, "Viral Marketing in Increasing Brand Awareness and Predicting Purchase Intention: Exploring Mediating Role of Brand Loyalty in FMCG Sector," Sch J Econ Bus Manag, vol. 4, pp. 61-77, 2023, doi: 10.36347/sjebm.2023.v10i04.001.
H. Ramadhani and N. Anggrainie, "Pengaruh Persepsi Harga, Brand Equity, Viral Marketing, Brand Ambassador, Review Produk, dan Customer Relationship, Terhadap Keputusan Pembelian Produk Skincare Skintific di Tiktok Shop," Mufakat: Jurnal Ekonomi, Manajemen dan Akuntansi, vol. 2, no. 4, pp. 703-717, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://jurnal.anfa.co.id/index.php/mufakat/article/view/983.
N. Barzegar Marvasti, "The Impact of Viral Marketing on Customer Purchase Intentions in Social Networks (Case Study: Tehran-based Users of Social Networks)," Master's Thesis, Shahid Beheshti University, 2015.
M. Ali Pour, F. Jafari, and A. Shafaqi Darvish Gournamaz, "Viral Marketing and Its Impact on the Success of Political Parties and Candidates in Electoral Competitions," Political Science Journal, no. 17, pp. 111-137, 2011.
F. Ohadi, M. Mohammadi, and M. Tarekh, "Evaluation of the Effectiveness of a Combined Viral Marketing Method with Network Clustering Method and Comparison of Results," Technology Growth Journal, vol. 15, no. 58, pp. 65-72, 2019.
I. Roelens, P. Baecke, and D. F. Benoit, "Identifying influencers in a social network: The value of real referral data," Decision Support Systems, vol. 91, pp. 25-36, 2016, doi: 10.1016/j.dss.2016.07.005.
K. Y. S. Putri, "Social Media or Word of Mouth: Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle During the COVID-19 Pandemic in Indonesia," International Journal of Innovative Research and Scientific Studies, vol. 7, no. 4, pp. 1345-1353, 2024, doi: 10.53894/ijirss.v7i4.3296.