Designing an Information Technology Strategic Plan (ITSP) in Knowledge-Based Industries of the Country Considering the Current National Economy
Keywords:
Information Technology, Strategic Plan, Knowledge-Based Industries, Pharmaceutical Industries, Interpretive Structural ModelingAbstract
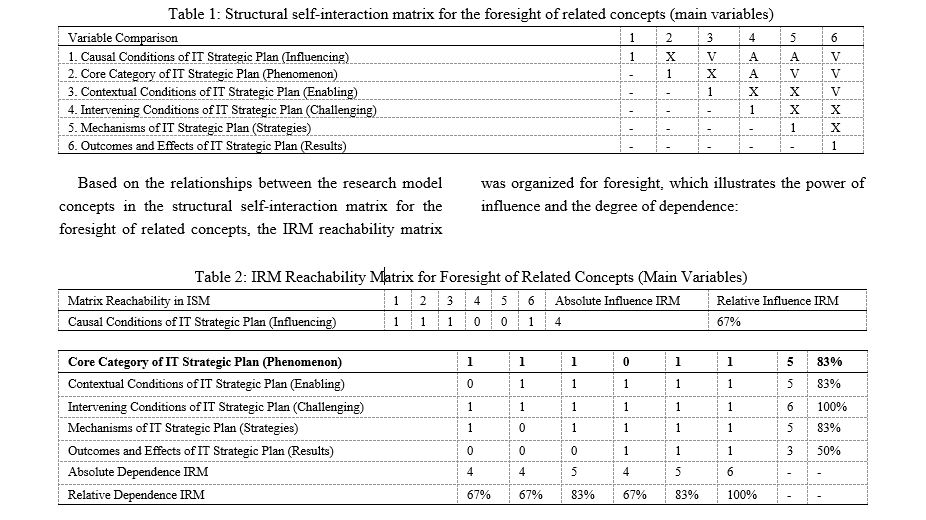
This paper aims to design an Information Technology Strategic Plan (ITSP) in the knowledge-based industries of the country, considering the current state of the national economy. The research is applied in nature and uses a mixed-methods approach (qualitative-quantitative) for data collection. The statistical population in the qualitative section includes 15 experts in knowledge-based pharmaceutical industries and academic experts. In the quantitative section, the participants consist of professionals and specialists working in the country's pharmaceutical industries, stakeholders from the public, and leading academic figures in the field. Ultimately, after distributing 106 instruments, the sample size of this study consists of 96 experts who were available and willing to participate, selected through a combination of non-probability purposive sampling (judgmental) and snowball sampling methods. The data collection tools were interviews in the qualitative phase and a researcher-made questionnaire in the quantitative phase. The validity and reliability of the questionnaire were confirmed. For data analysis, grounded theory, interpretive structural modeling (ISM) in the MicMac foresight matrix, and structural equation modeling (SEM) using AMOS software were employed. The results led to the identification of 18 components, including IT strategy evaluation; IT strategy formulation; IT strategy implementation; defining the organization's vision and goals; determining the organization's critical performance indicators; analyzing the organizational environment; strategic marketing orientation frameworks; IT strategic orientation frameworks; organizational strategic orientation frameworks; challenges related to organizational size; challenges related to the utilization of IT; challenges related to the type of industry; mechanisms for utilizing the internet infrastructure to provide organizational services anytime and anywhere; mechanisms for rapidly developing services and products for customers; mechanisms for addressing organizational needs in a competitive environment; enhancing IT governance; improving IT architecture; and implementing an IT infrastructure library. According to the reachability matrix calculations in interpretive structural modeling, the intervening conditions of the IT strategic plan (challenges) have the greatest influence, as their relative influence was calculated to be 100% (6 out of 6). In contrast, the outcomes and effects of the IT strategic plan (results) were determined to be 50% (3 out of 6). In fact, the relative influence and relative dependence for the contextual conditions of the IT strategic plan (enablers) and the mechanisms of the IT strategic plan (strategies) were measured to be exactly the same at 83%.