Design and Analysis of Automotive Supply Chain Enablers to Reduce the Bullwhip Effect Using Soft Systems Methodology, FCM, and ISM
Keywords:
Supply Chain, Bullwhip Effect, Enablers, Fuzzy Cognitive Mapping, Interpretive Structural Modeling (ISM)Abstract
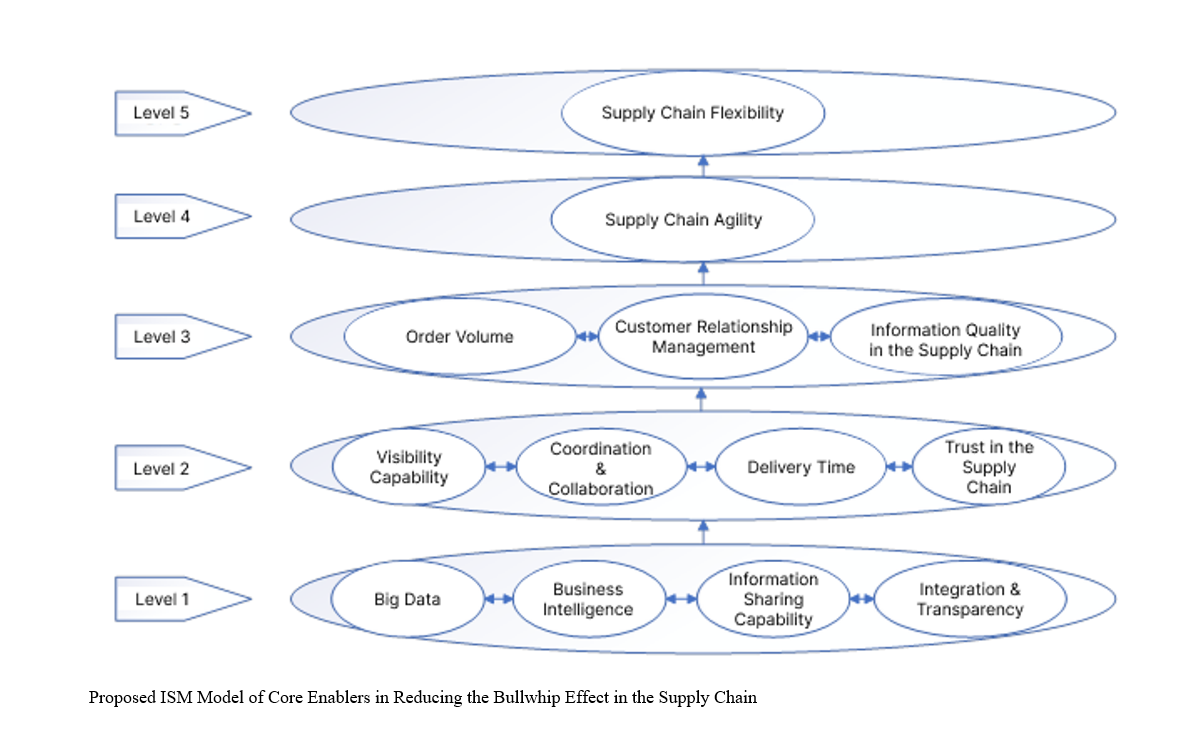
The supply chain inherently possesses a high degree of complexity, which has become increasingly exacerbated due to globalization, market expansion, and the continuous evolution of customer preferences. This growing complexity may lead to asset invisibility, inefficient inventory management, or logistical mismanagement. These complications often culminate in the well-known phenomenon of the "Bullwhip Effect" (BE) within supply chains. The aim of this study is to identify the key enablers that effectively reduce the Bullwhip Effect in the automotive supply chain sector. This research is descriptive in methodology and applied in purpose. To determine the importance of critical enablers influencing the mitigation of the Bullwhip Effect, a thorough review of the literature was first conducted to identify a preliminary list of significant enablers. Subsequently, using the Fuzzy Delphi Method, the final set of influential enablers for minimizing the Bullwhip Effect in the automotive supply chain was identified. To analyze the interrelationships among the 13 foundational enablers—based on literature and data collected through questionnaires—the study employed Fuzzy Cognitive Mapping (FCM) and Interpretive Structural Modeling (ISM) to determine the most impactful enablers. FCMapper software was used for the FCM method, while Excel software facilitated the ISM approach. Based on centrality metrics within the Fuzzy Cognitive Mapping approach, five enablers were found to be critically important: information quality in the supply chain, big data, supply chain flexibility, customer relationship management, and trust in the supply chain. Additionally, business intelligence, visibility capability, supply chain agility, order volume, information sharing capability, coordination and collaboration in the supply chain, supply chain integration and transparency, and delivery time were ranked sixth to thirteenth, respectively. According to the ISM results, the following enablers were identified in order of significance as the primary factors in reducing the Bullwhip Effect in the automotive supply chain: big data, business intelligence, information sharing capability, integration and transparency, trust in the supply chain, delivery time, coordination and collaboration, visibility capability, information quality, customer relationship management, order volume, supply chain agility, and flexibility.
References
F. Liu, M. Fang, S. Xiao, and Y. Shi, "Mitigating bullwhip effect in supply chains by engaging in digital transformation: the moderating role of customer concentration," Annals of Operations Research, pp. 1-22, 2024, doi: 10.1007/s10479-019-03363-3.
J. Gao, Y. Gao, T. Guan, S. Liu, and T. Ma, "Inhibitory influence of supply chain digital transformation on bullwhip effect feedback difference," Business Process Management Journal, vol. 30, no. 1, pp. 135-157, 2024, doi: 10.1108/BPMJ-01-2023-0029.
M. Wiedenmann and A. Größler, "The impact of digital technologies on operational causes of the bullwhip effect-a literature review," Procedia CIRP, vol. 81, pp. 552-557, 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.procir.2019.03.154.
M. Rezaeefard, N. Pilevari, F. F. Razi, and R. Radfar, "Factors Affecting Demand Predict to Reduce Bullwhip Effect in Supply Chain," Iranian Journal of Operations Research, vol. 13, no. 2, pp. 96-120, 2022.
R. Rossi, "Big data solutions towards the mitigation of the Bullwhip effect," 2022.
M. J. Alvarado-Vargas and K. J. Kelley, "Bullwhip severity in conditions of uncertainty: regional vs global supply chain strategies," International Journal of Emerging Markets, vol. 15, no. 1, pp. 131-148, 2020, doi: 10.1108/IJOEM-02-2017-0050.
J. Y. Zeng, C. H. Hsu, and X. Chen, "Using Agility to Reduce the Bullwhip Effect of Supply Chains," Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, 2022, doi: 10.1007/978-981-16-8048-9_5.
P. Borja, D. Roberto, C. Salvatore, and M. F. Jose, "The implications of batching in the bullwhip effect and customer service of closed-loop supply chains," International Journal of Production Economics, vol. 244, p. 108379, 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.ijpe.2021.108379.
G. Gaalman, S. M. Disney, and X. Wang, "When bullwhip increases in the lead time: An eigenvalue analysis of ARMA demand," International Journal of Production Economics, vol. 250, p. 108623, 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.ijpe.2022.108623.
D. J. Ghode, V. Yadav, R. Jain, and G. Soni, "Lassoing the bullwhip effect by applying blockchain to supply chains," Journal of Global Operations and Strategic Sourcing, vol. 15, no. 1, pp. 96-114, 2022, doi: 10.1108/JGOSS-06-2021-0045.
C. H. Hsu, X. H. Yang, T. Y. Zhang, A. Y. Chang, and Q. W. Zheng, "Deploying big data enablers to strengthen supply chain agility to mitigate bullwhip effect: An empirical study of China’s electronic manufacturers," Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research, vol. 16, no. 7, pp. 3375-3405, 2021, doi: 10.3390/jtaer16070183.
P. Ignaciuk and A. Dziomdziora, "Bullwhip effect-supply chain stability examination in the presence of demand uncertainty and delay," 2020 24th International Conference on System Theory, Control and Computing (ICSTCC), 2020, doi: 10.1109/ICSTCC50638.2020.9259768.
M. H. Khan, S. Ahmed, and D. Hussain, "Analysis of Bullwhip effect: A Behavioral Approach," Supply Chain Forum: An International Journal, pp. 1-22, 2019, doi: 10.1080/16258312.2019.1661756.
R. Raj, V. Kumar, and P. Verma, "Big data analytics in mitigating challenges of sustainable manufacturing supply chain," Operations Management Research, vol. 16, no. 4, pp. 1886-1900, 2023, doi: 10.1007/s12063-023-00408-6.
M. Nyamukoroso, "How big data characteristics can help the manufacturing industry mitigate the bullwhip effect in their supply chain," 2022.
D. Ojha, F. Sahin, J. Shockley, and S. V. Sridharan, "Is there a performance tradeoff in managing order fulfillment and the bullwhip effect in supply chains? The role of information sharing and information type," International Journal of Production Economics, vol. 208, pp. 529-543, 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.ijpe.2018.12.021.
C. I. Papanagnou, "Measuring and eliminating the bullwhip in closed loop supply chains using control theory and Internet of Things," Annals of Operations Research, vol. 310, no. 1, pp. 153-170, 2022, doi: 10.1007/s10479-021-04136-7.
M. Al-Sukhni and A. Migdalas, "Blockchain Technology for Information Sharing and Coordination to Mitigate Bullwhip Effect in Service Supply Chains," International Congress and Workshop on Industrial AI, 2021, doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-93639-6_17.
B. Sundarakani, A. Ajaykumar, and A. Gunasekaran, "Big data driven supply chain design and applications for blockchain: An action research using case study approach," Omega, vol. 102, p. 102452, 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.omega.2021.102452.
M. Sarkar, B. K. Dey, B. Ganguly, N. Saxena, D. Yadav, and B. Sarkar, "The impact of information sharing and bullwhip effects on improving consumer services in dual-channel retailing," Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, vol. 73, p. 103307, 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.jretconser.2023.103307.
T. Jafari, A. Zarei, A. Azar, and A. Moghaddam, "The impact of business intelligence on supply chain performance with emphasis on integration and agility-a mixed research approach," International Journal of Productivity and Performance Management, vol. 72, no. 5, pp. 1445-1478, 2023, doi: 10.1108/IJPPM-09-2021-0511.
S. Yang and L. Chen, "Bullwhip effect analysis for supply chains using a fuzzy forecast approach," 2021 33rd Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC), 2021, doi: 10.1109/CCDC52312.2021.9602212.
R. Watson, "Interpretive structural modeling—A useful tool for technology," Technological Forecasting and Social Change, vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 165-185, 1978, doi: 10.1016/0040-1625(78)90028-8.
P. H. Chen and P. L. P. Rau, "Evaluating Trust, Trustworthiness and Bullwhip Effect: A Three-Echelon Supply Chain Interactive Experiment," Cross-Cultural Design. User Experience of Products, Services, and Intelligent Environments, 2020, doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-49788-0_33.
A. Dolgui, D. Ivanov, and M. Rozhkov, "Does the ripple effect influence the bullwhip effect? An integrated analysis of structural and operational dynamics in the supply chain," International Journal of Production Research, vol. 58, no. 5, pp. 1285-1301, 2020, doi: 10.1080/00207543.2019.1627438.
G. Jiang, F. Liu, W. Liu, S. Liu, Y. Chen, and D. Xu, "Effects of information quality on information adoption on social media review platforms: Moderating role of perceived risk," Data Science and Management, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 13-22, 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.dsm.2021.02.004.
W. Jiang, "An intelligent supply chain information collaboration model based on Internet of Things and big data," IEEE access, vol. 7, pp. 58324-58335, 2019, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2913192.
G. Kankam, E. Kyeremeh, G. N. K. Som, and I. T. Charnor, "Information quality and supply chain performance: The mediating role of information sharing," Supply Chain Analytics, vol. 2, p. 100005, 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.sca.2023.100005.
E. Al Humdan, Y. Shi, and M. Behnia, "Supply chain agility: a systematic review of definitions, enablers and performance implications," International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management, vol. 50, no. 2, pp. 287-312, 2020, doi: 10.1108/ijpdlm-06-2019-0192.
V. P. Lele, S. Kumari, and G. White, "Streamlining Production: Using Big-Data’s CRM & Supply Chain To Improve Efficiency In High-Speed Environments," IJCSPUB-International Journal of Current Scienc (IJCSPUB), vol. 13, no. 2, pp. 136-146, 2023.
Z. Michna, S. M. Disney, and P. Nielsen, "The impact of stochastic lead times on the bullwhip effect under correlated demand and moving average forecasts," Omega, vol. 93, p. 102033, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.omega.2019.02.002.
W. Ran, Y. Wang, L. Yang, and S. Liu, "Coordination mechanism of supply chain considering the bullwhip effect under digital technologies," Mathematical Problems in Engineering, vol. 2020, pp. 1-28, 2020, doi: 10.1155/2020/3217927.
K. Ravi, O. Jan, A. Tarun Kumar, and W. Magnus, "The ABCDE of supply chain visibility: A systematic literature review and framework," International Journal of Production Economics, vol. 248, p. 108464, 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.ijpe.2022.108464.
A. Sarfaraz, R. K. Chakrabortty, and D. L. Essam, "A blockchain-coordinated supply chain to minimize bullwhip effect with an enhanced trust consensus algorithm," 2021.
A. Sarfaraz, R. K. Chakrabortty, and D. L. Essam, "The implications of blockchain-coordinated information sharing within a supply chain: A simulation study," Blockchain: Research and Applications, vol. 4, no. 1, p. 100110, 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.bcra.2022.100110.
L. Tang, T. Yang, Y. Tu, and Y. Ma, "Supply chain information sharing under consideration of bullwhip effect and system robustness," Flexible Services and Manufacturing Journal, 2020, doi: 10.1007/s10696-020-09384-6.
E. Weisz, D. M. Herold, and S. Kummer, "Revisiting the bullwhip effect: how can AI smoothen the bullwhip phenomenon?," The International Journal of Logistics Management, vol. 34, no. 7, pp. 98-120, 2023, doi: 10.1108/IJLM-02-2022-0078.
R. L. Bray, Y. Yao, Y. Duan, and J. Huo, "Ration Gaming and the Bullwhip Effect," Operations Research, pp. 1-15, 2019, doi: 10.1287/opre.2018.1774.
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Sadegh Danandeh (Author); Davood Talebi (Corresponding author); Mohammad Mehdi Movahedi (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.











