Minimizing The Delay and Energy Consumption in Cloud and Fog Hybrid Environments Based on The Timing of Requests in The IOT Using Plant Defense Optimization Algorithm
Keywords:
IoT, Optimization, Plant Defense Optimization (PDO), Fog Computing, Cloud ComputingAbstract
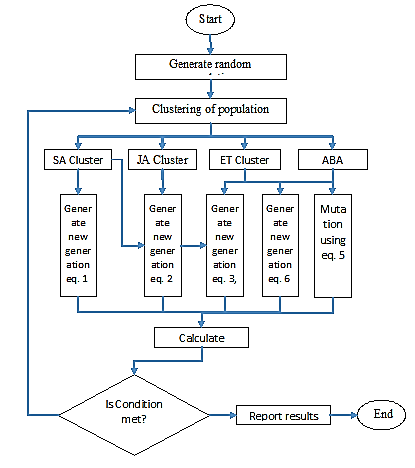
This study addresses the interaction between IoT devices and their physical environment, highlighting its role in minimizing delays in IoT applications. The core challenge lies in scheduling IoT requests and efficiently allocating them to Fog and Cloud resources while ensuring fault tolerance. To tackle these issues, an intelligent optimization method based on the Plant Hormonal Defense Optimization (PDO) algorithm is proposed. The PDO algorithm, enhanced by applying penalties to restrict infeasible solutions, offers a high-quality solution within a reasonable computation time. The method's performance is evaluated using key metrics, such as average total delay in relation to data volumes, the number of lost requests, the delay difference between Fog and Cloud layers when altering processing speeds in the Fog layer, the 90th percentile delay as the number of servers in the Fog layer changes, and both Fog and Cloud breakpoints.The PDO algorithm is tested in a simulated environment that mimics real-world dynamics. Comparative analysis shows that the proposed method reduces delays by 23.84% to 48.51% when compared to other algorithms, demonstrating its superior performance.