Providing a Causal Model of Industrial Resilience Using Thematic Analysis and Interpretive Structural Modeling in the Automotive Parts Manufacturing Industry
Keywords:
Industrial resilience, theme analysis, Interpretive structural modeling, auto parts manufacturing industryAbstract
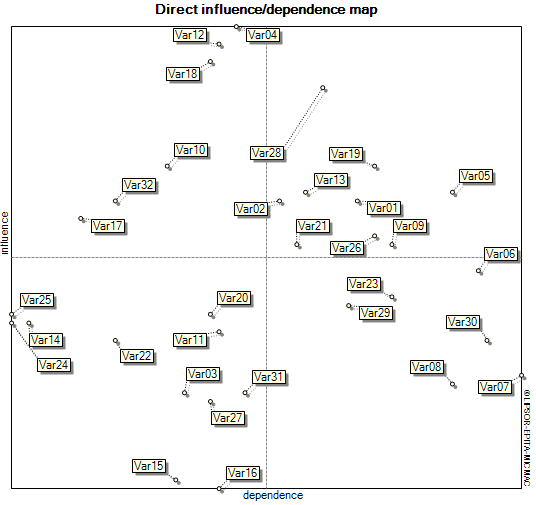
The aim of this study is to provide a causal model of industrial resilience using thematic analysis and interpretive structural modeling in the automotive parts manufacturing industry. The research approach is applied, and in terms of nature and method, it is descriptive-analytical and survey-based, falling under the category of mixed methods research (initially qualitative, followed by quantitative). Data and information were collected through a review of library and documentary sources and field observations (interviews and questionnaires). Quantitative models and software were employed for data analysis. Additionally, through thematic analysis and expert interviews, key drivers influencing industrial resilience were identified and selected. Based on the research findings, the overall pattern of industrial resilience drivers in the automotive parts manufacturing industry reflects an unstable environmental system, demonstrating an intermediate state of influence and susceptibility. To identify the relationships between variables and network resilience, the combined DEMATEL-ISM technique was utilized. The study's findings indicate 32 dimensions for designing the industrial resilience model. The results of interpretive structural modeling reveal that the factors of multiple suppliers and contractors, employee training, and knowledge transfer are the most influential components of the resilience model. Conversely, components such as facilitating inter-company collaboration, activities related to sales promotion, networking and cooperation with competitors, institutions, and research and knowledge-based organizations, product marketing and promotion, customer communication, and feedback reception are the most impacted components of the resilience model in the automotive parts manufacturing industry.
References
Z. Chen, "Sustainability Evaluation of Sports Tourism Using a Linguistic Neutrosophic Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Method," Plos One, vol. 19, no. 3, p. e0300341, 2024, doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0300341.
A. Di Leo, F. Sfodera, N. Cucari, G. Mattia, and L. Dezi, "Sustainability reporting practices: an explorative analysis of luxury fashion brands," Management Decision, vol. 61, no. 5, pp. 1274-1297, 2023, doi: 10.1108/MD-02-2022-0142.
C. S. Diepolder, "Exploring the Impact of Sustainable Entrepreneurial Role Models on Students’ Opportunity Recognition for Sustainable Development in Sustainable Entrepreneurship Education," Sustainability, vol. 16, no. 4, p. 1484, 2024, doi: 10.3390/su16041484.
A. Godha, "Examining the Role of Technological Advancements and Innovations in Enhancing the Sustainability Practices and Competitiveness of Certified B-Corps in India," Tfe, vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 28-36, 2024, doi: 10.46632/tfe/2/2/4.
G. Brundtland, Our Common Future: Report of the World Commission on Environment and Development. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press, 1987.
A. Tiernan, L. Drennan, J. Nalau, E. Onyango, L. Morrissey, and B. Mackey, "A review of themes in disaster resilience literature and international practice since 2012," Policy Design and Practice, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 53-74, 2019, doi: 10.1080/25741292.2018.1507240.
J. Fiksel, "Designing Resilient, Sustainable Systems," Environmental Science & Technology, vol. 37, pp. 5330-5339, 2003, doi: 10.1021/es0344819.
J. Fiksel, "Sustainability and Resilience: Toward a Systems Approach," Sustainability Science, Practice, and Policy, vol. 2, pp. 14-21, 2006, doi: 10.1080/15487733.2006.11907980.
L. Gunderson and L. J. R. Pritchard, Resilience and the Behavior of Large-Scale Systems. Washington, DC, USA: Island Press, 2002.
R. Martin, "The Roepke lecture in economic geography-rethinking regional path dependence: Beyond lock-in to evolution," Economic Geography, vol. 86, pp. 1-27, 2010, doi: 10.1111/j.1944-8287.2009.01056.x.
C. S. Holling, "Resilience and stability of ecological systems," Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, vol. 4, pp. 1-23, 1973, doi: 10.1146/annurev.es.04.110173.000245.
A. Pike, S. Dawley, and J. Tomaney, "Resilience, adaptation and adaptability," Cambridge Journal of Regions, Economy and Society, vol. 3, pp. 59-70, 2010, doi: 10.1093/cjres/rsq001.
L. Labaka, J. Hernantes, and J. M. Sarriegi, "A holistic framework for building critical infrastructure resilience," Technological Forecasting and Social Change, vol. 103, pp. 21-33, 2016, doi: 10.1016/j.techfore.2015.11.005.
R. Bhamra, S. Dani, and K. Burnard, "Resilience: The Concept, a Literature Review, and Future Directions," International Journal of Production Research, vol. 49, no. 18, pp. 5375-5393, 2011, doi: 10.1080/00207543.2011.563826.
J. Kay, "On complexity theory, exergy and industrial ecology: some implications for construction ecology," in Construction Ecology: Nature as a Basis for Green Buildings, C. J. Kibert, J. Sendzimir, and G. B. Guy Eds.: Spon Press, 2002.
A. Degeus, The Living Company. Cambridge, UK: Harvard Business School Press, 1997.
S. P. Gayialis, E. P. Kechagias, G. A. Papadopoulos, and E. A. Kanakis, "Smart-Contract Enabled Blockchain Traceability System Against Wine Supply Chain Counterfeiting," in IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology, 2022: Springer, Cham, Switzerland, pp. 477-484, doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-16407-1_56.
A. Rose and E. Krausmann, "An economic framework for the development of a resilience index for business recovery," International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, vol. 5, pp. 73-83, 2013, doi: 10.1016/j.ijdrr.2013.08.003.
T. J. Pettit, J. Fiksel, and K. I. Croxton, "Ensuring supply chain resilience: development of a conceptual framework," Journal of Business Logistics, vol. 31, pp. 1-21, 2010, doi: 10.1002/j.2158-1592.2010.tb00125.x.
C. S. Tang, "Robust strategies for mitigating supply chain disruptions," International Journal of Logistics: Research and Applications, vol. 9, pp. 33-45, 2006, doi: 10.1080/13675560500405584.
M. Christopher and H. Peck, "Building the Resilient Supply Chain," The International Journal of Logistics Management, vol. 15, pp. 1-14, 2004, doi: 10.1108/09574090410700275.
C. W. Craighead, J. Blackhurst, R. Handfield, and R. B. Handfield, "The Severity of Supply Chain Disruptions: Design Characteristics and Mitigation Capabilities," Decision Sciences, vol. 38, pp. 131-156, 2007, doi: 10.1111/j.1540-5915.2007.00151.x.
H. Peck, "Reconciling supply chain vulnerability, risk and supply chain management," International Journal of Logistics: Research and Applications, vol. 9, pp. 127-142, 2006, doi: 10.1080/13675560600673578.
H. Peck, "Drivers of supply chain vulnerability: an integrated framework," International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management, vol. 35, pp. 210-232, 2005, doi: 10.1108/09600030510599904.
A. Miceli, B. Hagen, M. P. Riccardi, F. Sotti, and D. Settembre-blundo, "Thriving, not just surviving in changing times: How sustainability, agility and digitalization intertwine with organizational resilience," Sustainability, vol. 13, p. 2052, 2021, doi: 10.3390/su13042052.
H. I. Lee, V. Padmanabhan, and S. Whang, "The bullwhip effect in supply chains," Sloan Management Review, vol. 38, pp. 93-102, 1997. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/227202717_A_review_of_the_causes_of_bullwhip_effect_in_a_supply_chain.
K. B. Hendricks and V. R. Singhal, "An empirical analysis of the effect of supply chain disruptions on long-run stock price performance and equity risk of the firm," Production and Operations Management, vol. 14, pp. 35-52, 2005, doi: 10.1111/j.1937-5956.2005.tb00008.x.
L. A. Bass and F. A. Boons, "An Industrial Ecology Project in Practice: Exploring the Boundaries of Decision-Making Levels in Regional Industrial Systems," Journal of Cleaner Production, vol. 12, pp. 1073-1085, 2004, doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2004.02.005.
J. Zhu and M. Ruth, "Exploring the resilience of industrial ecosystems," Journal of Environmental Management, vol. 122, pp. 65-75, 2013, doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2013.02.052.
B. Ida, Y. Teuku, and N. Rahmat, "Measuring Industrial Resiliency by Using Data Envelopment Analysis Approach," International Journal of Recent Technology and Engineering, vol. 7, no. 4S, 2018. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/331100684_Measuring_industrial_resiliency_by_using_data_envelopment_analysis_approach.
K. Cao, X. Feng, and H. Wan, "Applying Agent-Based Modeling to the Evolution of Eco-Industrial Systems," Ecological Economics, vol. 68, pp. 2868-2876, 2009, doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2009.06.009.
N. Bichraoui, B. Guillaume, and A. Holagh, "Agent-Based Modelling Simulation for the Development of an Industrial Symbiosis," in Procedia Environmental Science, 2013, vol. 17, pp. 195-204, doi: 10.1016/j.proenv.2013.02.029.
S. Lozano and A. Arenas, "A Model to Test How Diversity Affects Resilience in Regional Innovation Networks," Journal of Artificial Societies and Social Simulation, vol. 10, no. 4, p. 8, 2007. [Online]. Available: https://www.jasss.org/10/4/8.html.
W. A. Demmer, S. K. Vickery, and R. Calantone, "Engendering Resilience in Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs): A Case Study of Demmer Corporation," International Journal of Production Research, vol. 49, no. 18, pp. 5395-5413, 2011, doi: 10.1080/00207543.2011.563903.
A. Gunasekaran, K. R. Bharatendra, and M. Griffin, "Resilience and Competitiveness of Small and Medium Size Enterprises: An Empirical Research," International Journal of Production Research, vol. 49, no. 18, pp. 5489-5509, 2011, doi: 10.1080/00207543.2011.563831.
R. Pal, H. Torstensson, and H. Mattila, "Antecedents of organizational resilience in economic crises-an empirical study of Swedish textile and clothing SMEs," International Journal of Production Economics, vol. 147, pp. 410-428, 2018, doi: 10.1016/j.ijpe.2013.02.031.
H. Khwastar, "Investigation of factors affecting national self-efficacy in the field of science and technology to achieve visionary goals," Tehran University, 2017. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/322361693_Research_self-efficacy_and_its_relationship_with_academic_performance_in_postgraduate_students_of_Tehran_University_of_Medical_Sciences_in_2016